| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
- AuthenticatoinProvide
- SpringRESTDocs
- UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter
- SpringBoot
- T-OTP
- preventdefault
- Flyway
- OpenStack
- SWAGGER
- Crawling
- cloud native
- axios
- openapi3
- vuejs
- Filter
- Spring Security
- vue
- cheerio
- Reduxpender
- Spring REST Docs
- JavaScript
- 리액트
- REACT
- Pender
- MFA
- stopPropogation
- gradle
- MSA
- Spring Batch
- tasklet
- Today
- Total
Miracle Morning, LHWN
2. Mongoose 를 통한 MongoDB 연동 & 생성 (POST) 본문
Mongoose 란
Mongoose 는 MongoDB 기반의 ODM(Object Data Mapping) Node.js 전용 라이브러리이다.
ODM은 쉽게 말해 데이터베이스 <> 객체지향 프로그래밍 언어 사이에 호환되지 않는 데이터를 변환해주는 프로그래밍 기법이다.
즉, MongoDB 에 있는 데이터를 우리의 어플리케이션에서 JavaScript 객체로 사용할 수 있도록 해준다.
※ 프로젝트 생성 시 npm init 을 하면 package.json 이 생성된다.
프로젝트에 사용한 패키지들
# express : 웹 프레임워크
# body-parser : 데이터 처리 미들웨어 (req.body 를 통해 요청에 접근할 수 있게 해준다.)
# mongoose : MongoDB 연동 라이브러리
프로젝트 구조

# models : Data Schema 를 알려주는 파일이 속해있다.
MongoDB 연동 소스 (books API)
src/index.js
require('dotenv').config();
const Koa = require('koa');
const Router = require('koa-router');
const app = new Koa();
const router = new Router();
const api = require('./api');
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
const bodyParser = require('koa-bodyparser');
mongoose.Promise = global.Promise; // Node 의 네이티브 Promise 사용
// mongodb 연결
mongoose.connect(process.env.MONGO_URI,
{ useNewUrlParser: true, useUnifiedTopology: true }).then(
(response) => {
console.log('Successfully connected to mongodb');
}
).catch(e => {
console.error(e);
});
const port = process.env.PORT || 4000;
app.use(bodyParser());
router.use('/api', api.routes());
app.use(router.routes()).use(router.allowedMethods());
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log('heurm server is listening to port ' + port);
});
위 소스를 하나하나 뜯어보자.
require('dotenv').config(); .env 파일에서 환경변수를 불러온다.
// .env
PORT=4000
MONGO_URI=mongodb://localhost/heurmmongoose.Promise = global.Promise;mongoose 에서 데이터베이스에 요청을 할 때 Promise 를 사용할 수 있는데 이때 어떤 Promise 를 사용할지 정해주어야 한다.
Promise 에는 여러 종류의 구현체가 있는데 여기서 사용하는 Node 버전에서는 자체적으로 내장하고 있는 Promise 가 있기 때문에 리르 사용할 수 있도록 위와 같이 설정해준 것이다.
mongoose.connect(process.env.MONGO_URI,
{ useNewUrlParser: true, useUnifiedTopology: true }).then(
(response) => {
console.log('Successfully connected to mongodb');
}
).catch(e => {
console.error(e);
});이제 mongodb 에 연결을 해주는 것인데 connect() 메서드를 통해 서버에 접속을 한다.
(useNewUrlParser, useUnifiedTopology 옵션은 서버 실행 시 발생되는 오류를 제거하기 위해 추가해주었다.
useNewUrlParse 는 DB에 연결할 URI 에 대해 파싱을 하는 역할인데, 옵션의 이름이 최신화되어 발생했던 Warning 인 것 같다.)
const port = process.env.PORT || 4000;|| 연산자를 통해 PORT 값이 없다면 (false) 4000을 사용하겠다는 의미이다.
app.use(bodyParser());app 에 bodyParser를 적용하겠다는 의미이다. (단, 라우터 적용 코드보다 상단에 있어야 한다.)
bodyParser 를 사용하게 되면 POST 형식의 Request data 의 body 로부터 파라미터를 추출할 수가 있다.
req 파라미터가 body 라는 property 를 가지게 되는데 이 안에는 POST 방식으로 전달된 데이터가 json 형식으로 저장되어 있다.
router.use('/api', api.routes());api.routes() 의 내용을 /api 경로 하위 라우트로 설정하는 부분이다.
app.use(router.routes()).use(router.allowedMethods());OPTIONS 요청에 응답하고 405 (Method Not Allowed)나 501 (Not Implemented) 에러를 응답하는 별도의 미들웨어
src/models/book.js
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
const { Schema } = mongoose;
const Author = new Schema({
name: String,
email: String
});
const Book = new Schema({
title: String,
authors: [Author],
publishedDate: Date,
price: Number,
tags: [String],
createdAt: {
type: Date,
default: Date.now
}
});
module.exports = mongoose.model('Book', Book);여기에서 Author 은 Book 스키마에서 사용할 서브 다큐머트의 스키마이다.
...
author: [Author],
...# 스키마는 컬렉션의 문서에 어떤 종류의 값이 들어가는지를 정의하고,
모델은 스키마를 통해 만드는 인스턴스이다. 데이터에이스에 대한 실제 작업은 모델 객체를 통해 수행한다.
예)
var Blog = mongoose.model('Blog', blogSchema);이제 소스를 뜯어보자.
createdAt: {
type: Date,
default: Date.now
}스키마에서 기본 값을 설정해주고 싶을 때에는 { } 이렇게 객체로 설정해주면 된다.
module.exports = mongoose.model('Book', Book);
스키마를 model 로 변환한 후, 내보낸다 (exports).
첫 번째 파라미터는 스키마의 이름, 두 번째는 스키마 객체를 넣어주면 된다. 스키마의 이름을 정해주면 이의 복수형태로 컬렉션 이름을 만들어준다.
예를 들어 Book 으로 설정하면 실제 데이터베이스에 생성되는 컬렉션 이름은 books 이다.
데이터 생성 (POST)
src/api/books/book.controller.js
exports.create = async (ctx) => {
const {
title,
authors,
publishedDate,
price,
tags
} = ctx.request.body;
const book = new Book({
title,
authors,
publishedDate,
price,
tags
});
try {
await book.save();
} catch(e) {
return ctx.throw(500, e);
}
ctx.body = book;
};뜯어보자.
const {
title,
authors,
publishedDate,
price,
tags
} = ctx.request.body;request body 에 들어있는 객체의 값을 비구조화 할당을 통해 추출한다.
const book = new Book({
title,
authors,
publishedDate,
price,
tags
});추출한 값을 이용해서 Book 인스턴스를 만든다.
try {
await book.save();
} catch(e) {
return ctx.throw(500, e);
}save() 함수를 통해 데이터베이스에 실제 데이터를 작성하는 부분이며, save() 함수는 Promise 를 반환한다.
만일 저장에 실패하면 catch 를 통해 HTTP 500 (Internal Error) 메시지를 반환한다.
POSTMAN 으로 POST 요청해보기
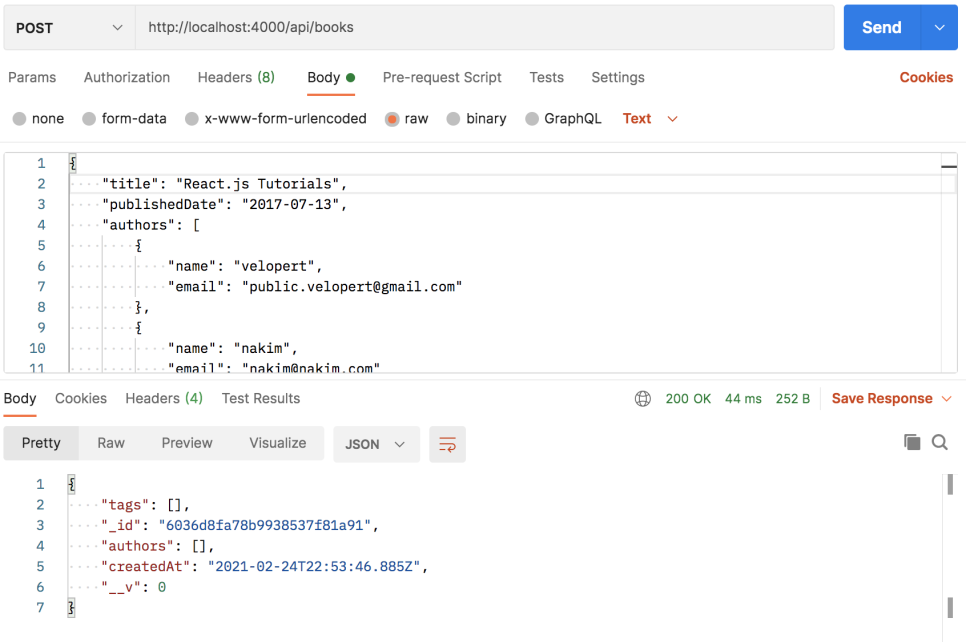
근데 왜 여기서 /api/books 를 통해 요청을 하는걸까?

위 구조를 보면 알겠지만 src/index.js 에서 const api = require(./api); router.use('/api', api.routes()); 를 해주었다.
즉, /api 에 대한 요청은 api.routes() 경로에서 사용하겠다는 의미이다.
그리고 또 다시 api/index.js 에서 const books = require('./books'); api.use('/books', books.routes()); 를 해주었다.
즉, /books 에 대한 요청은 books.routes() 경로에서 사용하겠다는 의미이다.
또 다시 books/index.js 를 보면 이제서야 비로소 books.post('/'. booksCtrl.create); 를 해주고 있다.
왜냐하면, 특정 디렉토리에 있는 index.js 파일은 디렉토리 자체를 의미하기 때문이다.
require 할 때도 './api/index.js' 가 아닌 './api' 처럼 폴더만 require 해주어도 자동으로 index.js 파일에 접근한다.
출처 : https://backend-intro.vlpt.us/2/05.html
2-5. 데이터 생성과 조회 · GitBook
2-5. 데이터 생성과 조회 이제 데이터베이스를 연동하여 books API 의 기능을 구현해보겠습니다. 먼저, books.controller.js 파일의 상단에 아까 우리가 만든 모델을 불러와주세요. src/api/books/books.controller
backend-intro.vlpt.us
'IT 기술 > [React] Project' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [오류] /bin/sh: react-scripts: command not found (0) | 2021.06.01 |
|---|---|
| 2_0. 조회(GET), 삭제(DELETE), 수정(PUT, PATCH) (0) | 2021.06.01 |
| 1_0. 이것저것 궁금해서 찾아본 것들 정리 (0) | 2021.06.01 |
| 1. Node.js express 프레임워크의 session (0) | 2021.05.31 |
| 0_0. 환경 세팅하면서 이것저것 궁금해서 찾아본 것들 정리 (0) | 2021.05.31 |

